- Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, offers an enticing opportunity for investors to profit from the fluctuations in currency values. However, successful trading in the forex market requires a keen understanding of various economic indicators and their impact on stock markets. In this blog, we delve into the significance of economic indicators in forex trading and explore key takeaways for aspiring traders.
Impact of Economic Indicators on Stock Markets:
Interest Rates
- One of the most influential economic indicators is interest rates. Central banks regularly adjust interest rates to control inflation and stimulate economic growth. Higher interest rates attract foreign capital, leading to an appreciation of the currency. Conversely, lower interest rates tend to depreciate the currency. Forex traders closely monitor central bank announcements regarding interest rate changes as they can significantly affect currency values.

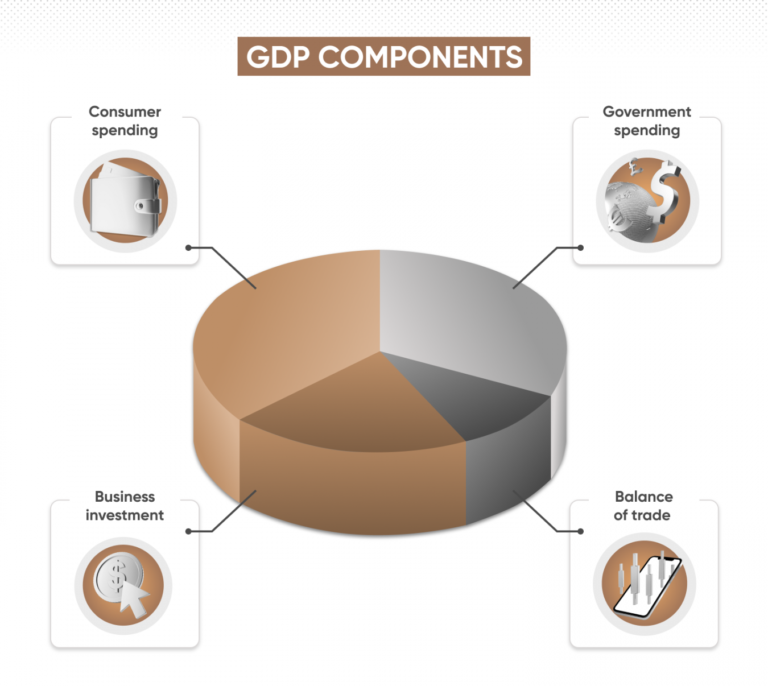
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
- GDP measures the total value of goods and services produced within a country's borders. A strong GDP growth rate indicates a robust economy, which can strengthen the currency. Conversely, a decline in GDP growth may lead to currency depreciation. Forex traders analyze GDP reports to gauge the overall health of an economy and make informed trading decisions.
Employment Data
- Employment indicators, such as non-farm payroll reports and unemployment rates, provide insights into the labor market's health. Positive employment data, such as a decrease in unemployment rates or an increase in job creation, typically strengthens the currency as it signals economic growth and consumer spending. Conversely, rising unemployment rates may lead to currency depreciation.
Inflation Rates
- Inflation measures the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising. Central banks aim to maintain moderate inflation levels to ensure price stability. High inflation rates erode purchasing power and can lead to currency depreciation. Forex traders monitor inflation reports and central bank statements to assess the likelihood of interest rate adjustments, which can impact currency values.

Trade Balance
- The trade balance reflects the difference between a country's exports and imports. A positive trade balance, where exports exceed imports, typically strengthens the currency as it indicates strong international demand for goods and services. Conversely, a negative trade balance may lead to currency depreciation. Forex traders analyze trade balance data to assess a country's competitiveness in the global market and its currency's potential direction.

Key Takeaways
- 1. Stay Informed: Successful forex trading requires staying informed about economic indicators and their potential impact on currency values. Traders should regularly monitor economic calendars, central bank announcements, and relevant news sources to make informed trading decisions.
- 2. Understand Interconnections: Economic indicators do not operate in isolation. They are interconnected, and changes in one indicator can influence others. Traders should analyze the broader economic landscape to understand the potential implications for currency markets.
- 3. Manage Risk: Forex trading involves inherent risks, and economic indicators can introduce volatility into the market. Traders should employ risk management strategies, such as setting stop-loss orders and diversifying their portfolios, to mitigate potential losses.
- 4. Adaptability is Key : Economic conditions are constantly evolving, requiring traders to adapt their strategies accordingly. Flexibility and the ability to react swiftly to changing market dynamics are essential for success in forex trading.
- 5. Utilize Technical Analysis : While economic indicators provide valuable insights, traders can complement their analysis with technical indicators and chart patterns to identify potential entry and exit points. Combining fundamental and technical analysis can enhance trading strategies.